Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
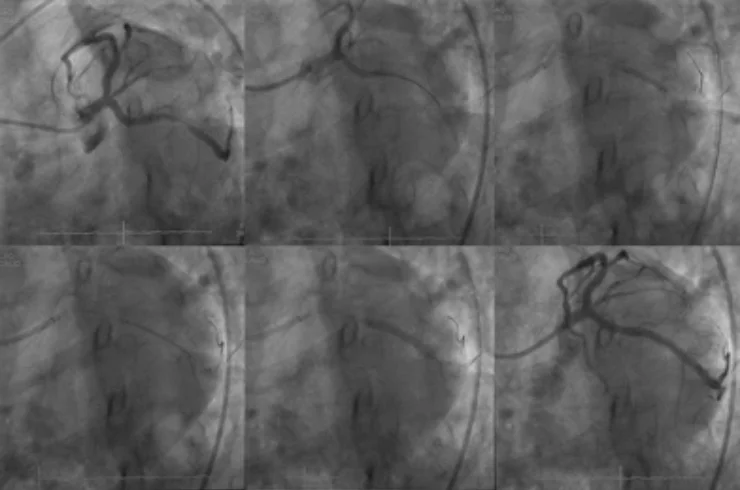
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI), commonly known as Coronary Angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), a condition where the coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup. This blockage restricts the blood flow to the heart, which can cause chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or even lead to a heart attack. PCI is performed to open up these blocked arteries and restore normal blood flow, significantly improving heart health.
At Kurnool Cardiac Center, under the expert care of Dr. Nagendra Prasad Thota, we specialize in performing PCI using the latest techniques and advanced medical technology. Our goal is to ensure your heart receives the best care, allowing you to live a healthier and more active life.
What is Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)?
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) is a non-surgical procedure used to treat coronary artery blockages. It involves inserting a catheter (a thin, flexible tube) through a small incision, typically in the groin or wrist, and guiding it to the blocked coronary artery. Once the catheter reaches the blockage, a small balloon at the tip of the catheter is inflated, which compresses the plaque against the artery wall, widening the artery and restoring blood flow to the heart.
In most cases, a stent (a small mesh-like device) is also placed in the artery to keep it open after the balloon is deflated and removed. The stent acts as a scaffold to prevent the artery from narrowing again, ensuring long-term blood flow.
Why is PCI Performed?
PCI is primarily performed to relieve symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease, such as:
- Chest Pain (Angina): The heart doesn’t get enough oxygen-rich blood, causing discomfort or pain in the chest.
- Shortness of Breath: Reduced blood flow can make it harder for the heart to pump effectively, leading to breathing difficulties.
- Heart Attack Prevention: PCI is often used to prevent a heart attack by opening a blocked artery and restoring normal blood flow.
In many cases, PCI is recommended for patients with significant coronary artery blockage or those who have experienced a heart attack.
How is PCI Performed?
The PCI procedure is typically done in a catheterization lab (cath lab) and involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The patient is given local anesthesia to numb the insertion site (usually in the groin or wrist). A catheter is then inserted into a blood vessel and guided to the site of the blockage.
- Balloon Angioplasty: Once the catheter reaches the blockage, a balloon at the tip is inflated. This opens up the blocked artery, compressing the plaque against the artery walls.
- Stent Placement: If necessary, a stent is placed into the artery to keep it open after the balloon is removed.
- Post-Procedure Monitoring: After the procedure, patients are closely monitored for a short period to ensure there are no complications.
Benefits of PCI
- Restores Normal Blood Flow: PCI helps to open blocked arteries, allowing for better blood flow to the heart, which relieves chest pain and improves heart function.
- Minimally Invasive: Unlike traditional bypass surgery, PCI is a less invasive procedure, meaning smaller incisions, less pain, and a quicker recovery.
- Prevents Heart Attack: By restoring normal blood flow, PCI can prevent further damage to the heart and reduce the risk of a heart attack.
- Faster Recovery: Most patients experience a quicker recovery with PCI than they would with open-heart surgery. Many patients can return to normal activities within a few days to weeks.
Risks and Potential Complications
While PCI is generally a safe procedure, as with any medical intervention, there are risks involved. Some potential complications include:
- Bleeding: There is a risk of bleeding at the catheter insertion site.
- Blood Clots: Blood clots can form around the stent, potentially leading to re-blockage.
- Restenosis: Sometimes, the artery can become narrowed again over time, especially if a bare-metal stent is used.
- Vessel Injury: In rare cases, the catheter or balloon may cause damage to the blood vessel.
Your cardiologist will discuss these risks with you and take steps to minimize them, such as prescribing medications to prevent blood clots and monitoring you closely after the procedure.
Post-Procedure Care
After PCI, you will be monitored in the hospital for a few hours to ensure that there are no complications. For the best results and to reduce the risk of future heart issues, you may be advised to:
- Take Medications: Blood thinners or antiplatelet medications are commonly prescribed to prevent blood clots from forming around the stent.
- Adopt Healthy Lifestyle Changes: A healthy diet, regular physical activity, and smoking cessation are essential to keeping your heart healthy.
- Follow-up Care: Regular check-ups with your cardiologist are important to monitor your heart health and ensure the stent is functioning properly.
Why Choose Kurnool Cardiac Center for PCI?
At Kurnool Cardiac Center, we are committed to providing high-quality care for patients with heart conditions. Here’s why you should trust us for your PCI procedure:
- Experienced Cardiologists: Dr. Nagendra Prasad Thota, with years of experience in interventional cardiology, leads our team in providing the best possible treatment for coronary artery disease.
- Advanced Technology: We use the latest technology and techniques to ensure that PCI is performed with precision and minimal discomfort.
- Comprehensive Care: From diagnostics to rehabilitation, we provide a complete range of services to support your heart health.
- Patient-Centered Approach: Your well-being is our priority. We offer personalized care and guidance throughout your treatment journey.
Treatments
- ECG
- 2D Echo
- TMT (Treadmill Test)
- Angiogram
- Angioplasty
- Bypass Surgery
- Heart Failure
- Valvular Heart Diseas
- Arrhythmias
- Cardiomyopathy
- Congenital Heart Defects
- Lipid Disorders
- Coronary Artery Disease
- Coronary Angioplasty and Stenting
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
- Mitral Valve Repair or Replacement
- Atrial Septal Defect Closure
Consult Kurnool’s Leading Heart Specialist
Reach out to Kurnool Cardiac Center and meet Dr. Nagendra Prasad Thota for advanced diagnostics and treatment.
